HOW TO CARE FOR MAPLE TREES
Maple trees are deciduous trees that belong to the Acer genus and are widely known for their beauty and ornamental value.
Maple trees are native to the Northern Hemisphere and are found in regions with temperate climates, including North America, Europe, and Asia.
They are valued for their striking fall foliage, which turns bright shades of yellow, orange, and red before dropping in the autumn.
Every season we offer a wide selection of maples and Japanese maples to choose from.

Acer spp – Background
There are about 132 species of maple in this genus.
Roots – These deciduous trees have a dense fibrous root system that can make it difficult to plant underneath them especially as they grow older. It is best not to plant silver maples near foundations as they can cause damage. Most of us are familiar with surface hugging silver maple roots as they age. These roots spread far and wide!
Sugar and Japanese maple roots on the other hand rarely cause damage. They tend to be more fragile and less invasive.
Leaves – Maple trees have an opposite leaf arrangement, and their veins are palmate and lobed in most species.
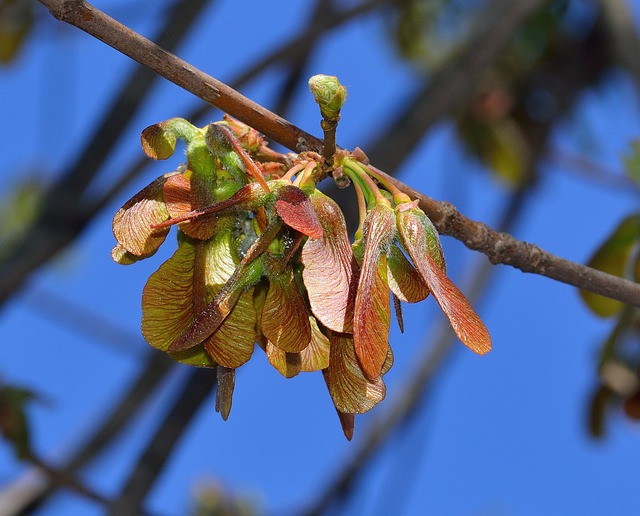
Seed and flowers – Seeds are known as samaras. Commonly, they are often referred to as “helicopters” or whirybirds”.
Flowers are laregly insignificant for gardening purposes – though many are a great resource for pollinators.
Preferred soil
Maple trees can grow in a variety of soil types, but they prefer well-drained, moist, and slightly acidic soils. A soil pH between 5.5 and 6.5 is ideal for most maple species. However, some species, such as the sugar maple, prefer a slightly more acidic soil with a pH of around 5.0 to 6.0.
Maple trees also benefit from soils that are rich in organic matter and nutrients. Adding compost, peat moss, or other organic matter to the soil can help to improve its structure and fertility, making it easier for the tree to absorb the nutrients it needs to grow and thrive.
Note: For newly planted trees,do not let the soil dry out – especially during the hot summer months!
Pruning
When considering how to care for maple trees, pruning is important for maintaining their health, improving their structure, and controlling their growth. Here are some general guidelines for pruning maple trees:
- Timing: Prune maple trees in late winter or early spring, before new growth begins. You can do light pruning during the growing season.
- Dead and diseased wood: Remove any dead, diseased, or damaged wood, as well as any crossing or rubbing branches. These can be sources of infection or weakness that can harm the tree.
- Crown thinning: Thin out the upper branches of the tree to increase air flow and light penetration, which can help to prevent disease and promote healthy growth.
- Crown reduction: If necessary, reduce the overall size of the tree by removing the tops of branches. This should only be done on a limited basis and with caution, as it can be stressful for the tree.
- Cutting: Make all cuts cleanly and just above a bud or side branch. Avoid leaving stubs, which can be sources of decay and entry points for pests and diseases.
See our guide: HOW TO PRUNE TREES AND SHRUBS.
Diseases
Maple trees can be susceptible to a variety of diseases, some of the most common include:
Verticillium Wilt: This is a fungal disease that affects the water-conducting vessels of the tree, causing yellowing and wilting of leaves (due to lack of water and nutrients), especially on one side of the tree.
One of the key diagnostic features of Verticillium wilt in maple trees is the presence of dark streaks or discoloration in the wood of affected branches or stems. This discoloration is caused by the fungal infection, which blocks the tree’s vascular system and prevents water and nutrients from reaching the leaves and other parts of the tree.
Leaf Spot / Tar Spot: This is a fungal disease that causes dark spots to form on the leaves of the tree, which can eventually turn yellow and fall off.
Anthracnose: This is a fungal disease that causes leaf blotches and premature defoliation, particularly in cool, wet springs.
Powdery Mildew: This is a fungal disease that causes a white, powdery growth on the leaves and shoots of the tree.
Leaf Scorch: Hot, dry summer weather causes the tree’s leaves to turn yellow and brown along the margins, eventually leading to premature defoliation.
Preventative measures include proper watering and maintenance, selecting disease-resistant varieties, and promptly removing and destroying infected leaves or branches. In some cases, fungicides can be used to treat the diseases.
For the most part, especially as maples mature, they will survive most minor diease infections..
How To Care For Maple Trees
– Spectacular Japanese maples and water garden! –

